Impressions are rising, but clicks are decreasing. Year over year, your site performance looks like it’s declining. Meanwhile, Google is adding new AI features to Chrome. In fact, every search engine is right now.
Right now, our clients want to know how AI overviews are impacting their marketing. Is SEO dead? Is Google dead? Should you even produce content?
So let’s dive into the most frequently asked questions around AI overviews, SEO, and what that means for your content marketing.
First, Let’s Define AI Language

FAQs About AI Overviews Impact On SEO & Marketing
1. Are traditional search engines (like Google) still important?
The best way to answer this question is to regularly evaluate your traffic in Google Analytics, or whatever tool you use. Study where your traffic is coming from. Note changes or shifts.
Focus your efforts on the channels you already see users coming from, because that tells you where your audience spends their time.
Recently, I looked at 2024 vs 2025 data for a client. While they’re seeing more traffic from AI referrals, the majority of traffic to their site is still coming from search engines. For example, 11K sessions to blogs came from a traditional search, while 300 came from an AI referral.
That said, are search behaviors changing? Absolutely. My message this year has been that the places and ways we can search are fracturing.
For example, more people are searching Reddit because they want insights from real people. ChatGPT released Atlas. Pinterest is more of a search engine than it is a social platform. Instagram posts now show in search results.
That’s why it’s important to use real data to evaluate which platforms you need to focus on in your SEO strategy. And build your strategy across all channels, not just one.
2. Can I see where I’m showing up?
There are a few tools right now. One of the more trustworthy ones is Semrush’s AI Toolkit. I’ve also had hit-or-miss experiences with SpyFu’s SpyGPT tool. (If your brand has a more local reach, you may have a harder time getting results.)
Another workaround is to isolate referral traffic in your GA4 reporting from popular AI sites. This will measure visits from citations, but it still can’t offer you insights into brand mentions.
Specifically for Google, AI mode counts toward any totals you see in your Search Console reporting. That said, there’s nothing in place yet to filter and only see AI mode impressions, clicks, and other data.
Some of this is likely due to the extreme personalization AI search accommodates. And the way it’s integrated into the search experience. The setup makes isolating and collecting data complex. Some of these companies may also be viewing AI overviews as an evolution of search, making them hesitant to start treating AI like its own channel/source.
Want to make sure you’re showing up where your audience is online?
3. How can I tell if AI overviews are affecting my traffic?
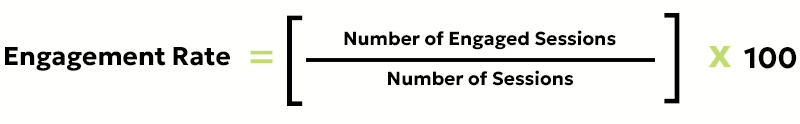
Zero-click marketing. If you notice your site content is getting more impressions and fewer clicks, it’s a sign you’ve been impacted. AI overviews are contributing to that.
Here’s an example of what our SEO team has been calling the “alligator mouth.” In their AI overview analysis, they noticed this trend starting across all our clients when features in Google search become more integrated during April 2025.

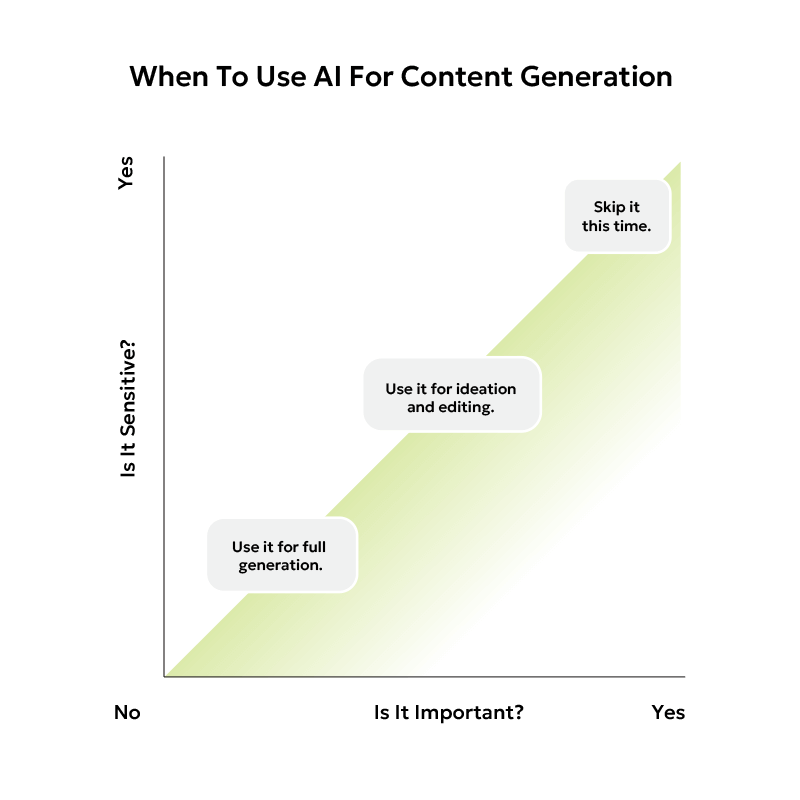
4. Is content even relevant anymore?
Content is always relevant. It’s currency! However, what that content looks like should evolve. Match what people enjoy consuming. (Remember how early Facebook used to be all text posts? Content changes.)
Plus, content provides context on what you do. And context is key for increasing your chances of ranking in AI overviews.
A regular search engine ranks pages primarily on keywords and link authority. (With a few other mysterious ingredients in the mix that we’re not privy to.)
But AI ranks based on contextual information, expertise, entity authority, and also its understanding of the user and what they’re searching for. Its goal is to deliver a personalized answer and results can look wildly different between users, even with the same prompt.
It’s time we reframe our thinking in marketing content.
Blogs are a piece of the puzzle. We don’t expect users to read the whole article anymore. They’re great because they feed AI context, which can help with getting an AI citation.
But other content that’s equally important now includes:
- Case studies or project examples
- PDFs and rich multimodal resources
- Video
- Infographics
- Real photography (not stock)
- Specialized landing pages outside your core site pages
- Resource hubs and collections
Also, sometimes businesses look at content with a narrow perspective, only focusing on its value in search. This misses its potential. A good content strategy helps your brand by:
- Helping prospective clients discover you
- Supporting the selling process
- Providing something valuable to your email subscribers
- Engaging your current clients to foster loyalty
- Making it easy for others to recommend your brand
- Creating a memorable experience around receiving a product or service
5. How can I rank and appear in AI overviews?
The path forward here is less certain than SEO. AI search is changing rapidly right now, making it hard to answer. But in 2025, Google gave us some hints.
I’ve also been recommending the following tips. In my experience, the clients who were already doing this are the ones who are getting marketing results from AI overviews.
- Keep content fresh. Update top-performing content around 6-12 months.
- Create a lot of context with diverse types of content.
- Produce a lot of content to build up that context around who you are.
- Craft longer pieces (like blogs) and answer a lot of niche questions.
- Boost your authority and recognition with reviews, social signals, etc.
- Show proof of what you do with real-world examples.
- Execute SEO best practices, like making sure crawlers can find your content and having structured data that matches it.
Want to scale your content production, but make sure you’re still creating pieces that have value?
The Takeaway: All LLMs Are Not Equal
Semrush has been collecting data on the differences between LLMs. They’ve related the era we’re in now to the early days of Google and Yahoo when they had different algorithms.
For example, their team has noted that Perplexity is more likely to pull a summary from citations and share the source. Gemini often gives sources in its AI overviews and in initial answers. However, ChatGPT doesn’t typically give links until the 3rd or 4th prompt.
It’s still too early to optimize for each LLM. We don’t know all the factors yet, and the LLMs themselves are still developing. The best choice right now is to focus on what’s a smart marketing strategy to begin with. Because of all the changes happening in search, we’ll have to rethink how we measure marketing attribution in the years to come.
But for now, the way to win with AI overviews, SEO, and content is to focus on what’s best for the person who is using it. If you pursue that instead of focusing on gaming the system, you’ll stay ahead of the changes just fine.