If you haven’t checked out our blog on the biggest Google SERP (search engine results page) changes, you’ve missed out on a visual timeline representing the changes on Google’s search results page since it’s introduction in 1998 — and it has changed a lot!
Twenty years later, there are many instances in which a user doesn’t even need to click off the results page to find the information they need. That’s great for the user, but not so great for companies trying to drive traffic to their websites. Companies who have reached the coveted #1 organic rank in a Google search might now find that they are listed a third of the way down the page, buried under a slew of prioritized Google SERP features or other types of rich results.
Here are a few of the Google features that have become staples of the SERPs, along with tips on using these rich results to get noticed by an online audience.
Paid Advertising
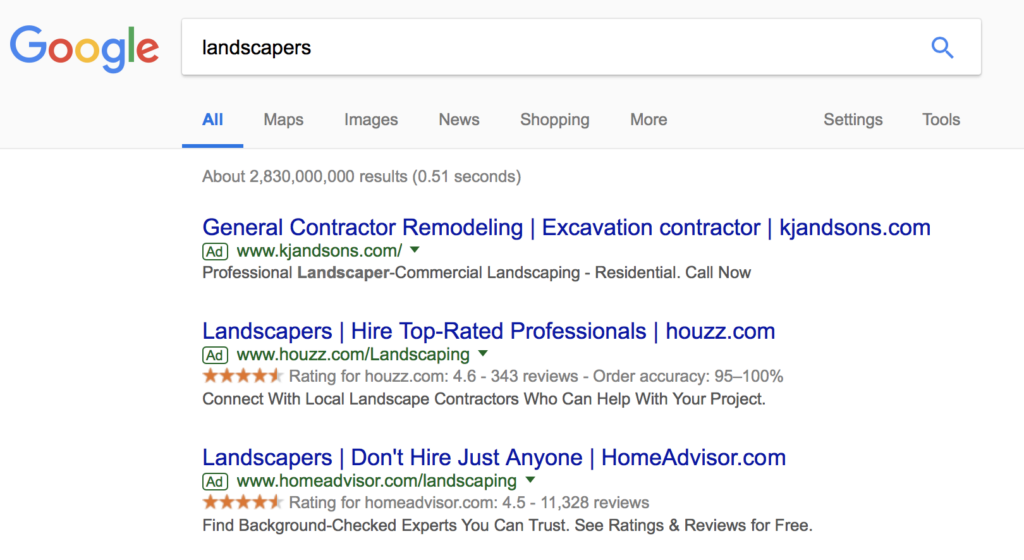
Google Ads may not seem too unfamiliar to web users. Typically, companies that are running Google PPC (pay-per-click) campaigns will have their ads featured at the very top of a Google search page.
Give Your Ads The Best Chance of Being Seen:
Paid advertising campaigns can be beneficial by gaining web traffic in support of a newly launched website, your business’s peak seasons, or a big sale or major event. A paid advertising campaign can also give you insights into the keywords for which your website is being found. These insights go beyond what you can find through Google’s standard reporting,
Follow these tips for better paid advertising placement:
- Your keyword quality score should be at least a 3 out of 10. Low-quality ad scores usually result in low click-through rates. For a higher score, avoid keywords that are too generic, use long-tail keywords, and make sure your keywords mirror your ads and landing page.
- Watch the character counts in your ads. Your title should be no more 30 characters and your description include a maximum of 80 characters. Going beyond the suggested character count can result in key information being cut off in your ads.
- Include additional site links in your ad copy to increase the click-through rate on your ads, which Google favors in ad placement.
- Add call-out extensions. For example, Sale Ends on Monday, 15% Discount on Kids Shoes, etc.
Local Listings
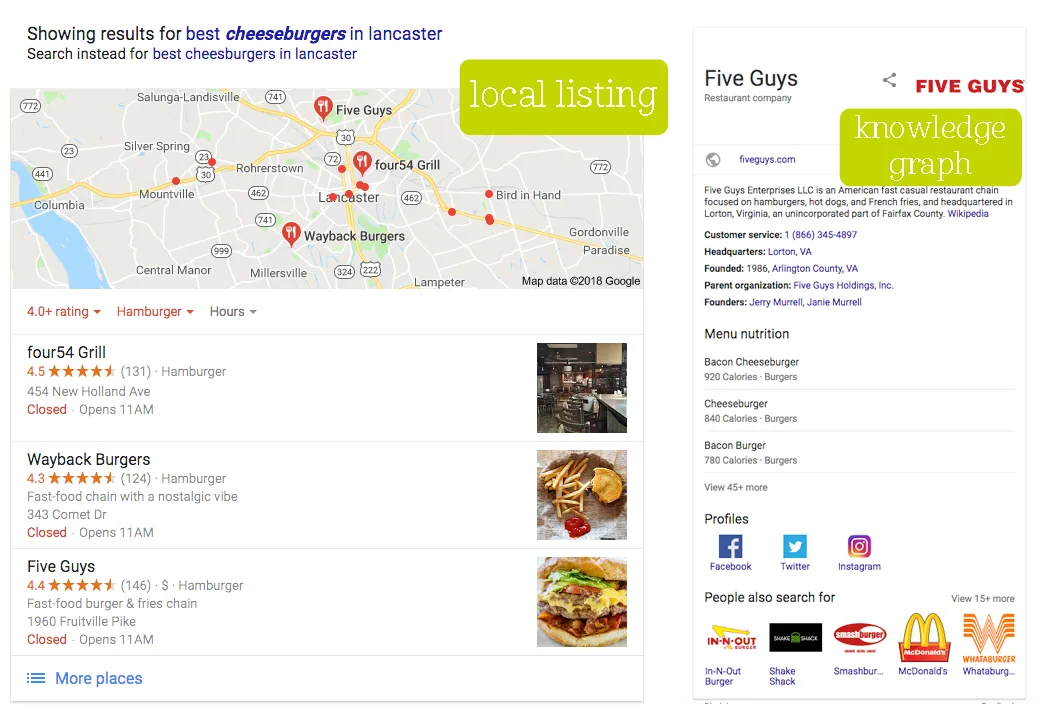
The next SERP feature that you may notice is local listings which include the local pack and local listing knowledge graph. These are especially helpful to users with the rise of “near me” searches; for example “find cheeseburgers near me.”
The local pack includes a local map based on a user’s location with two or more nearby options for what they need. This gives users everything they need at a quick glance, including the address, hours, and the company’s Google review rating.
The knowledge graph, which is typically located in the right column of the results page, is a large component in many search results. It also offers the most requested information about your company’s physical location at a quick glance (address, hours, phone number, map). Links to your website and directions to your location are also included.
Make Sure Your Business Shows in Local Listings:
For your business to show up in local searches, one of the very best tools to utilize is MozLocal. With a MozLocal account, you can use the most important online business directories and review sites to find any inaccuracies or duplicate listings. These issues can arise due to mix-ups with user-generated check-ins or multiple employees attempting to set up your business in the same directory.
In addition, you’ll want to claim your Google My Business listing and optimize your listing with the most up-to-date information on your business including service area, hours, phone number, website URL, images, and videos.
A My Business listing is will most likely show up in the SERPS during branded searches (the user searches specifically for your brand name). You can increase your opportunities for being found in non-branded searches by adding category tags to your My Business Listings. For example, restaurant, fast food restaurant, or hamburger restaurant.
Additionally, you can use these tips to help your site land among the local listings by:
- Creating content on key web pages (homepage, about us page, and other popular landing pages) that ties into your location.
- Responding to Google Reviews for your business (the good and the bad) with sincere and unique responses. Not only does this show customers that you respect their feedback, but Google also takes this into account and can tell when you’re repeating the same canned responses.
- Reviewing the suggested edits that users can submit to your MyBusiness listing based on their experiences. You have the ability to accept or deny these user updates.
Want to learn more about local listings? Read more about local SEO directories in our guide which includes the top free and paid listings to put your business on.
Featured Snippets
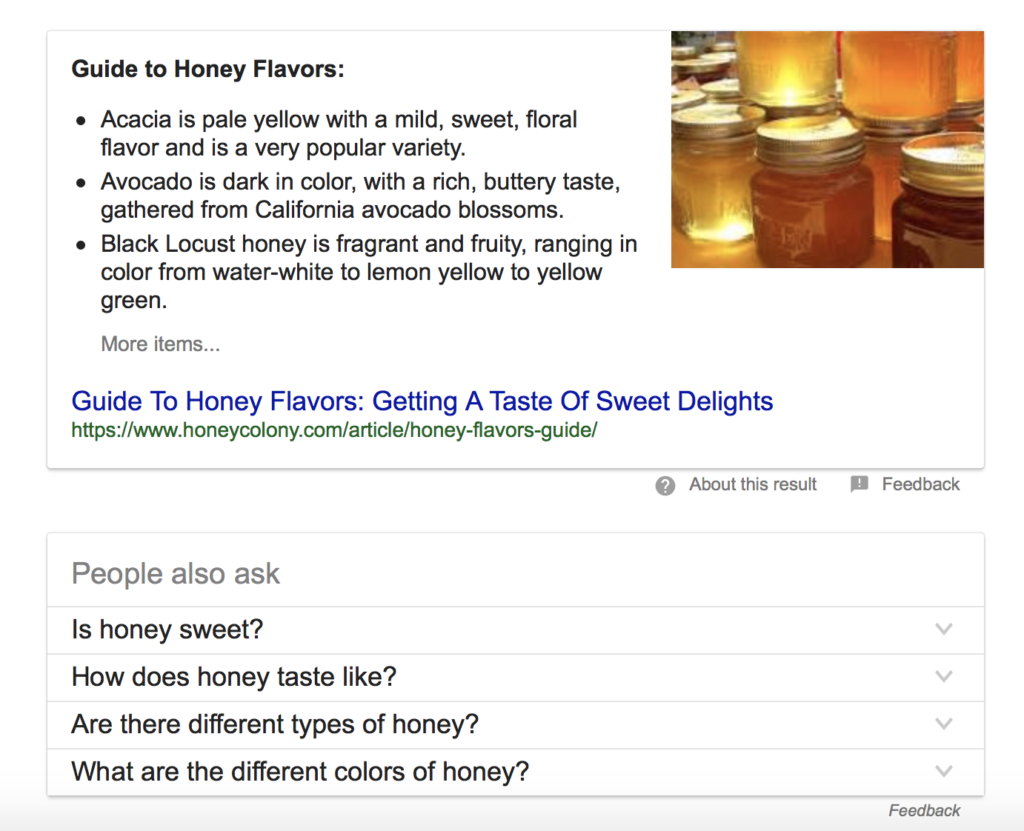
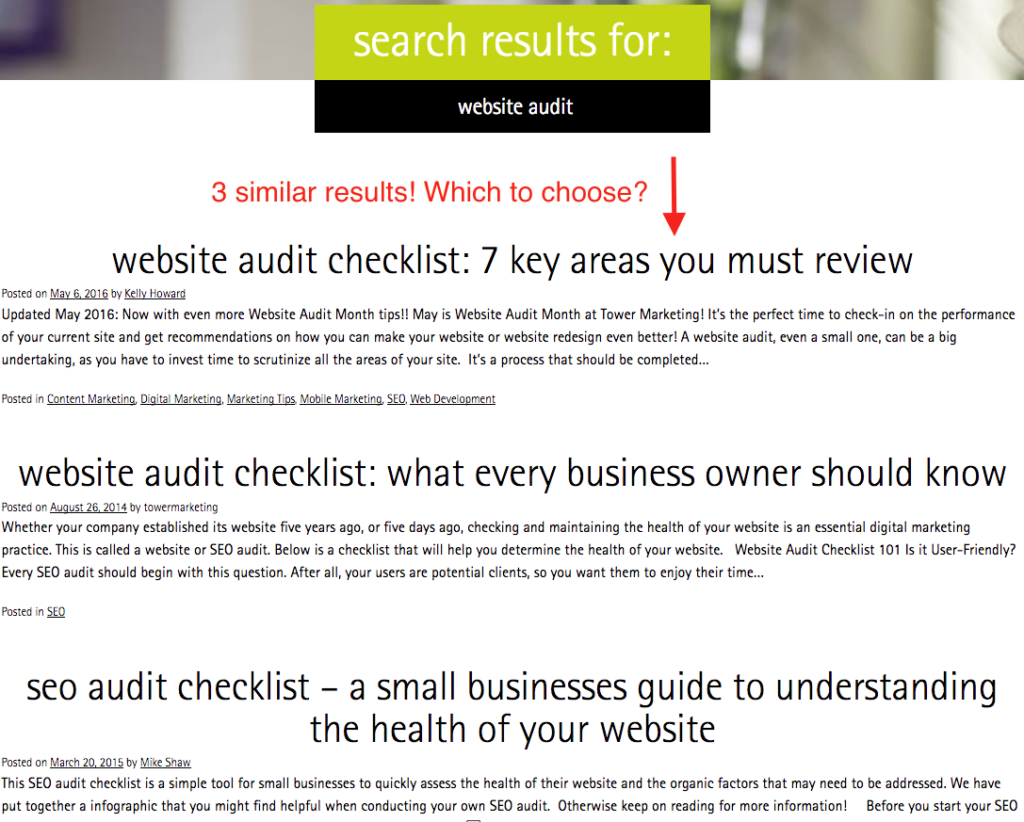
Here’s where things start to get tricky when your goal is increasing web traffic. With the introduction of Google’s featured snippets, users don’t need to click-thru to your site to find the answers you’re providing. Much of it is being displayed right on the Google search page. It’s why this feature is also called the “answer box.” Not only that but if the original answer that Google provides doesn’t suit a user’s needs, it offers multiple other questions and answers that a user can also read right on the search page.
Although featured snippets provide quick results that may negatively impact click-through rates, SEO experts see it as a positive feature. Snippets can improve overall site rankings and help a website acquire more SERP real estate. For example, if your organic results rank is position 8, but your information is presented as a featured snippet, you can outrank competitors and improve click-through.
Make Your Website a Featured Snippet:
The chance to be spotlighted in a featured snippet is dependent on the content you publish on your site. Content that is presented in a question and answer format is often displayed as part of a snippet. But don’t overdo it, you’re not going to fool Google!
Additional content best practices to follow include:
- Formatting that includes subheadings and bulleted or numbered lists.
- Optimizing your content, images, and metadata for important keywords.
- Using variances of your keywords.
Finally, adding schema to your pages that highlights the main question and answer can make it easier for Google to zero-in on your page as a source of information that users are searching for.
Other Google SERP Features to Know
These additional features also help your website claim more real estate throughout the SERPs.
Site Links — Google site links are a deluxe listing format that presents the main search result, followed by two or more indented site link results.
Image Pack — Optimizing your images with keyword-driven alt text will give you a better chance of appearing in Google Images, which are often highlighted on a search results page.
Videos — To entice user click through, Google will add a video thumbnail to the top YouTube results for a particular search.
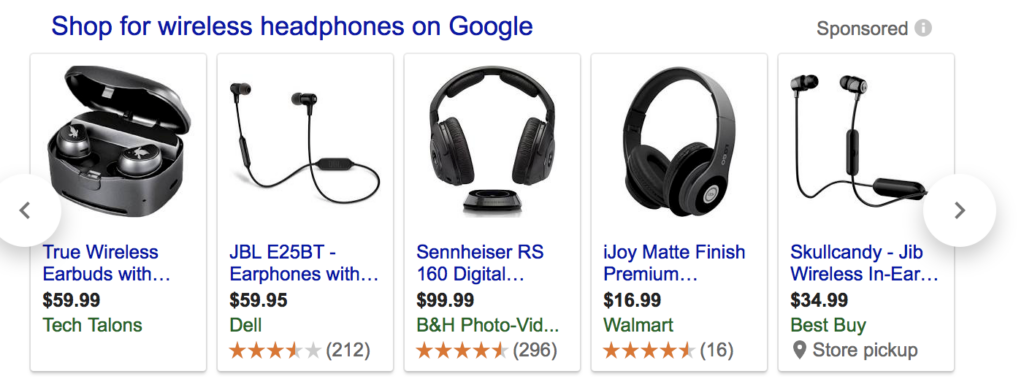
Shopping Carousel — Google’s shopping feature takes a standard text-ad PPC campaign and enhances it by including additional snippets of information (image, price, ratings, etc) from the product page.
What to learn more about getting found in the Google SERPS? Visit our SEO services page to see how we can help your business get found!
photo credit: www.quotecatalog.com