The Digital Marketing Mix: How the 4Ps Have Evolved in the Age of Internet Marketing
- Branding
- Marketing Strategy

If you work in business, you’ve probably heard the terms “marketing mix” or “the 4Ps of traditional marketing” at one point in time. But with the booming success we’ve seen in the digital marketing industry, have you considered how to integrate those concepts into your internet marketing strategy?
Learn how the digital marketing mix uses the 4Ps —plus 3 additional Ps — to master the nuances of successful online marketing.
The 4 Ps of the Traditional Marketing Mix
The traditional marketing mix is defined by Phillip Kotler as a “set of marketing tools that the firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.” That “set of marketing tools” is what’s commonly referred to as the 4Ps.
The 4Ps are the foundation of any successful marketing plan. They include:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
For years, the 4Ps have been the go-to model for building a marketing strategy. But, in the era of internet marketing, referring to only the 4 Ps can limit your brand’s reach.
According to WordStream by LocaliQ, 72% of marketing budgets are reserved for digital channels, increasing digital marketing’s share of advertising to 55%. With that increase, the concepts of product, price, place, and promotion also needed to grow.
The digital marketing mix is an expansion of Kotler’s traditional marketing tools. The 7 Ps of digital marketing include product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence.
Defining The 7Ps of The Digital Marketing Mix
Let’s jump into defining the digital marketing mix and explaining how using these 7Ps can help you build on your existing approach to better reach your customers.
1. Product
Product refers to the ‘thing’ you offer that your target audience wants. This can be a physical, tangible item, or an intangible service. From clothing or water bottles to home insurance or a digital marketing agency, a product is the item or service the user seeks to fill a need.
If it helps, think of the product in terms of supply and demand. All consumers have wants and needs. You are in business because you offer something that is wanted or needed by a consumer. Your product supplies that consumer’s demand.
Focus on the Consumer First
A lot of businesses think they have a great product and then try to market it to the public and fail. Harvard Business School professor, Clayton Christensen, reports that over 30,000 new products are launched every year, only 5% of which succeed.
Most times, it’s because of poor market research. They have not asked the fundamental question: Why do people want this?
If there’s no need for your product, it won’t sell. Understand the consumer demand first and then design your product around that need. From there, identify your unique selling point (USP) that makes your product valuable to buyers and differentiates you from competitors.
Product Questions to Ask Yourself:
- What does the customer want from my product? What need(s) does it satisfy?
- What is my USP?
- What advantages does my product offer to meet the user’s needs?
- How do I differentiate my product/service from competitors?
- Are there features a competitor product has that mine does not? Are there features that the consumer does not deem valuable or worth paying for?
- Does my product have a name? How is it branded?
- How do I intend consumers to my your product? Are they using it correctly? Where will they use it?
Answering these questions can help you understand the end user’s view of your product and can help drive additional marketing decisions because you understand what problem your product solves.
2. Price
Price is what the consumer is willing to pay for your product. While it’s a generally easy concept to understand, it can be tricky for many businesses to apply — prices that are too high push users to search elsewhere; prices that are too low cut into your profit margins.
Understanding your target audience and the relationship between perceived benefits, price, and value can help simplify the process. If perceived benefits increase or price decreases, the perceived value should generally go up. But if perceived benefits decrease or the price increases, the perceived value goes down.
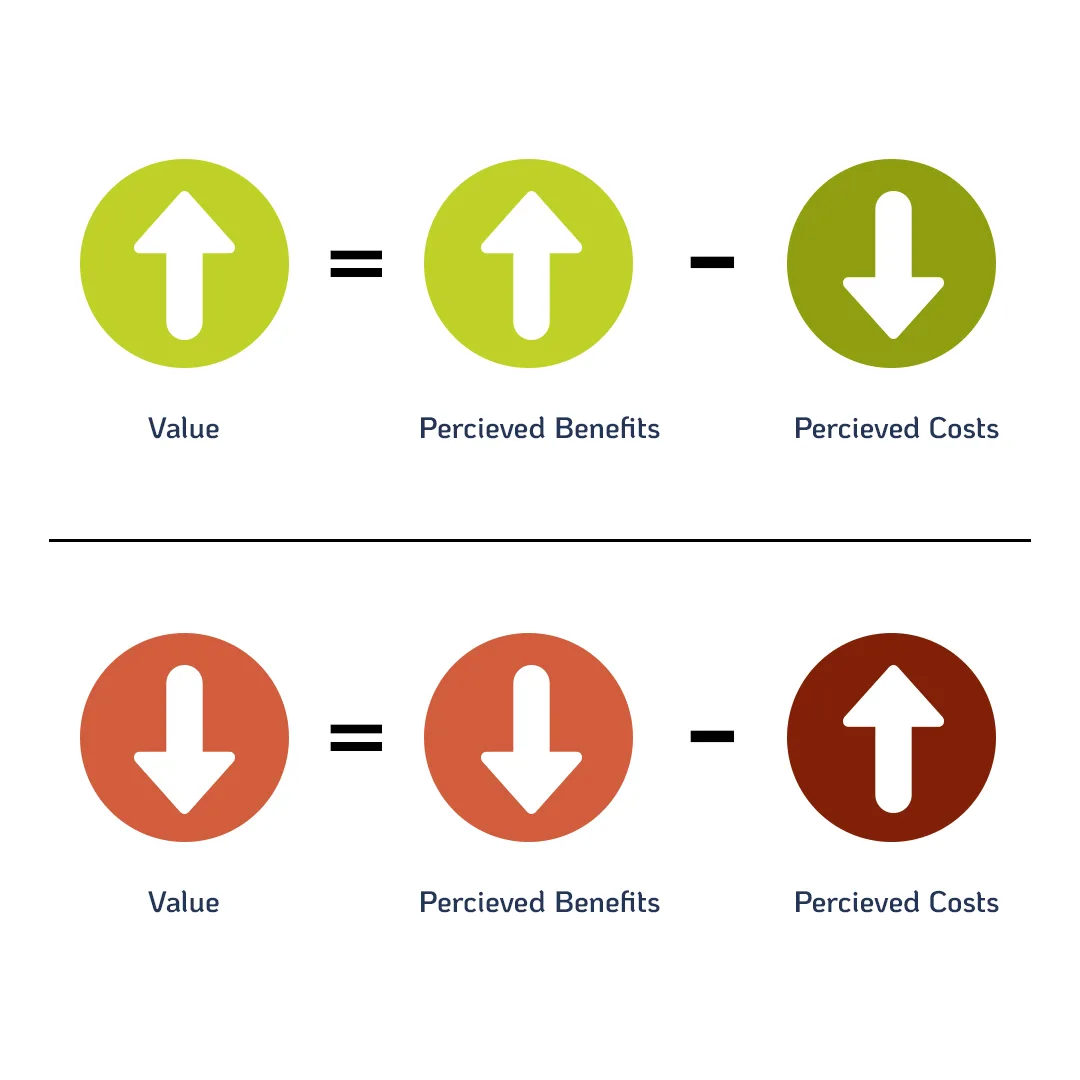
If consumers don’t see any perceived benefits in your product, or if they decide the benefits aren’t worth the price, your product’s value will decrease and you’re less likely to make sales.
Opportunity Cost
Since a large part of the pricing model relies on what consumers perceive as valuable, your business needs to understand what the consumer feels they are losing out on by choosing your product over the others — also known as the opportunity cost.
Here’s an example: I have $350. I can spend it on Facebook ads that might generate leads, or I can use it on Google text ads. If I spend the money on Google ads then I forfeit the opportunity Facebook ads might bring in. The loss of those potential Facebook leads is the opportunity cost.
In this situation, I have to make the decision of what I find more valuable. Will Google or Facebook get me the leads I need? Which is the most cost-effective? Which is easier to manage? Where is my target audience most likely to be?
Your customers will ask themselves similar questions before making a purchase: will this product make my life easier? Am I getting my money’s worth? If you can anticipate those opportunity costs, you can use them to your advantage to choose a price that’s appropriate in your market.
Factors That Affect Product Pricing:
There are so many factors that can impact the price of your product, some of the most common including
- Competitive offerings and prices
- Market share
- Product branding and quality
- Materials or input costs
- Customers’ perceived product value and fair price.
Depending on the factors that are most important to you and your target market, you can price your product appropriately using one of the following approaches:
- 1. Demand-oriented pricing: set the price based on the demand for the product or service. If demand is high, consumers might be willing to pay more for the product.
- 2. Cost-oriented pricing: consider how much it costs to make your product and markup accordingly so you see a profit.
- 3. Profit-oriented pricing: determine your business’s profit goals and test out prices that yield your desired return on sales (ROS).
- 4. Competition-oriented pricing: price your product similarly to your competitors to compete with their market share.
Pricing Questions to Ask Yourself:
- What is my product’s perceived value in the eyes of the consumer?
- What is the lowest cost I can charge while still selling enough to be profitable?
- Is my target market price-sensitive? What effect will changes in price do in the marketplace?
- Should I increase or lower the price?
- Are my prices competitive?
Don’t forget to also consider making adjustments to your price. Seasonal discounts, trade-in deals, and other cost-saving measures can prove to be successful in many markets. Make sure you have a plan in place to monitor your price to handle the ebbs and flows of demand.

3. Place
Place refers to where the consumer is able to purchase your product. It solves the complicated process of getting the product from the manufacturer into the hands of buyers.
Traditionally, place referred to strictly brick-and-mortar locations. But the internet has added some complexities to this principle of the digital marketing mix, opening the door for many more distribution channels to meet consumers where they are.
Ecommerce sites can be an incredibly useful place to sell your product. In 2021, retail eCommerce retail sales exceeded $5 trillion US dollars globally — a number that’s projected to rise above $8 trillion by 2026.
If your site is lacking online retail capabilities or you’re not selling your product through third-party marketplaces online, you’re limiting your place strategy. It’s one of the easiest ways to increase your brand’s reach.
Places and Accessibility
Smartphones (and the internet in general) allow the consumer to have a 24/7 marketplace accessible from anywhere at any time. It is critical that your brand exists in the digital space. Not only that, your business should easily found and active in that space.
Examples of Online Places Include:
- Websites displaying interactive ads
- Search engines highlighting shopping ads
- Google search results
- Emails
- Social channels such as Facebook, Instagram, or Pinterest
Making your products accessible to the users at a time and place that is most convenient to them will give your business a competitive advantage.
Place Questions to Ask Yourself:
- Where is my target market searching for products? Are consumers looking in brick-and-mortar stores? Online? Direct sales?
- Do I have access to the medium or channel? Do you have expertise and knowledge of how these channels perform? Can I optimize the efficiency of these distribution channels?
- Where are my competitors most active? Where do they push their products? Are they utilizing a channel that I‘m not?
Because there are so many more “locations” or channels for the consumer to find your product, deciding on the placement of your product can be a challenge. It’s crucial that you get to know your target audience to determine which distribution channels are most likely to convert into a lead or sale.
4. Promotion
Jim Blyth defines promotion as “the marketing communications used to make the offer known to potential customers and persuade them to investigate it further.” Simply put, it’s your strategy for getting people to notice your product or service.
Thanks to modern technology, businesses have more channels than ever to communicate through. A few examples can include Google My Business listings, sponsored ads, Instagram posts, email newsletters, and much more.
These tools can help your brand personalize your marketing by tailoring your message to a specific user. Using GA4 and consumer engagement reports, you can even determine where your audience is most active and segment them according to mobile devices, browsers, and operating systems.
Which Channels to Use
When deciding on distribution channels, it’s important to make sure it fits your audience and your brand. Here are some major online distribution channels:
- Search Engines
- Organic search results (e.g. Google and Bing)
- Paid/sponsored listings (e.g. Google and Bing)
- Display Ads
- Banner Ads
- Interactive Ads
- Social Media (posts and Ads)
- YouTube
- Digital word-of-mouth
- Forums (e.g. Reddit)
- Wikis
- Influencers (e.g. bloggers)
- Business listing (e.g. Yelp)
Promotion Questions to Ask Yourself:
- What potential channels are available to communicate my message?
- Where are my competitors promoting their products or services? Where are they active that we’re not?
- Which is the most effective channel to communicate through?
- What is an appropriate cadence for our promotion?
How you choose to promote your product or service can make all the difference in converting leads into sales.
5. People
In the digital marketing mix, people refers to anyone who represents your product and comes in contact with the consumer. Aside from your customer service team or sales force, people can include your employees, business partners, or anyone that consumers associate with your brand.
It’s important you’re hiring people who understand your brand’s vision and believe in your goals. You should be able to trust that when they come in contact with customers, they’re representing your brand in a positive light.
This is increasingly important if your brand is on social media.
Social Media Relationships
Social media, online forms, emails, and other internet platforms have created a way to interact with customers directly. These added relationship factors give your brand the ability to:
- Respond quickly to users asking questions on Facebook, Instagram, Reddit, etc.
- Add insightful recommendations via Quora
- Respond to negative reviews on Google Reviews or Yelp
Businesses that are utilizing these platforms can leverage the power of relationship-building where customers are active. Interacting with your customers directly on these platforms can strengthen trust and keep consumers coming back to your brand.
People Questions To Ask Yourself:
- Do my employees understand our brand identity?
- Do my business partners understand our company goals?
- Is our company culture positive?
- Are my employees skilled in basic social media strategy?
- Have I set clear expectations for my employees to follow when interacting with customers?
The bottom line: your people represent your brand. How they interact with customers can make or break their perception of your product or service.

6. Process
Process is defined as the core tasks and operations required to deliver the product or service to your customer. This can refer to anything from logistics and shipment and delivery to wait times and check-out processes.
If your customers find your processes to be too complicated — for instance, the time from placing an order to receiving it is too long — you’re likely to lose out on future sales.
To optimize your processes and create the best experience for your potential customers, it’s critical to understand the user journey. If you can simplify the sales funnel and make the process from initial brand discovery to purchasing feel natural, the greater your chances are to convert.
Process Questions To Ask Yourself:
- How easy is it to navigate through our website? Is it easy to make a purchase online?
- How long are our delivery times? How does this compare to competitors?
- Do we have enough staff to cover the amount of purchases/requests being made?
- Are there any internal process barriers keeping us from delivering customer value?
- Have our customers complained about our process? Where are they dissatisfied?
Listening to customer feedback can be a really useful tool for defining your process strategy. Take customer complaints as an opportunity to reevaluate your current process and strategize how to fix it.
7. Physical Evidence
The final P in the digital marketing mix is physical evidence. It’s the proof that your product or service exists and is credible. In the online universe, your brand’s digital footprint can serve as your physical evidence.
Your website is the most important measure of physical evidence for most people. If it’s up-to-date and easy to navigate, your brand can seem more trustworthy.
Personal touches like thank you notes, confirmation emails, and receipts after a purchase can be another piece of physical evidence to keep your brand top-of-mind for customers.
Additionally, it’s important your brand is represented on social media. You should be prioritizing creating solid brand awareness across multiple platforms and channels. Existing on these platforms and staying active can build credibility.
Physical Evidence Questions To Ask Yourself:
- What post-purchase procedures do we have in place? Is there anything we could improve on?
- Are we represented across multiple channels? Is our branding consistent across each?
- Does our website provide a positive first impression? Is the UX positive?
- Are we actively responding to customers on social media or via email?
The more time you spend expanding your message across multiple channels and platforms can greatly increase the value the customer finds in your brand, product, or service.
An Integrated Marketing Approach is Best
Increase your share of voice by choosing an integrated marketing approach. When you start using the 7Ps of the digital marketing mix, you can multiply your reach using a consumer-centric strategy.
Digital Marketing Mix Checklist
- Identify the product or service. What is the Unique Selling Proposition (USP)?
- Research and understand your target audience. Who are your potential customers? What do they search for? Is your product relevant to their needs?
- Research and understand your competition. Is the market highly competitive or are you a pioneer? What can you learn from other businesses competing in this space?
- Assess the channels (space) where your customer engages with your product. Understand the pros and cons of each platform/place.
- Test your digital marketing mix. Ask customer-focused questions:
- Does the product meet the user’s need(s)? (Product)
- Is the pricing right? Or does it need to change? (Price)
- Where are the consumers? Are your marketing channels delivering as expected? (Place)
- Is your marketing message resonating with the target audience? Do they understand? Do they feel confident in making a purchase? (Promotion)
- Do my employees positively represent our brand? (People)
- Is it easy to purchase and receive our product/service? (Process)
- Can we be found across multiple marketing channels? (Physical Evidence)
- Review your marketing plans & adjust each of the elements to cater to your user, market, and business needs.
Need help implementing an integrated approach to your marketing plan? Our digital marketing team has been solving that problem for our clients for over 25 years. Contact our team for a consultation.
Editor’s note: This blog was originally published on June 16, 2020. It was updated on July 28, 2023.
 By Ali
By Ali  Grace Z
Grace Z  Danae
Danae