As technology advances so do the skills of internet ne’er-do-wells and other sorts of villainy. In fact, cyber-attacks are very lucrative for criminals and extremely costly for its victims.
Depending on the attack, the goal may be to just add a site or server to a botnet army to be used against larger prey, or the attack may be aimed at getting information from your business. Here are a few common types of cyber attacks that you need to be aware of:
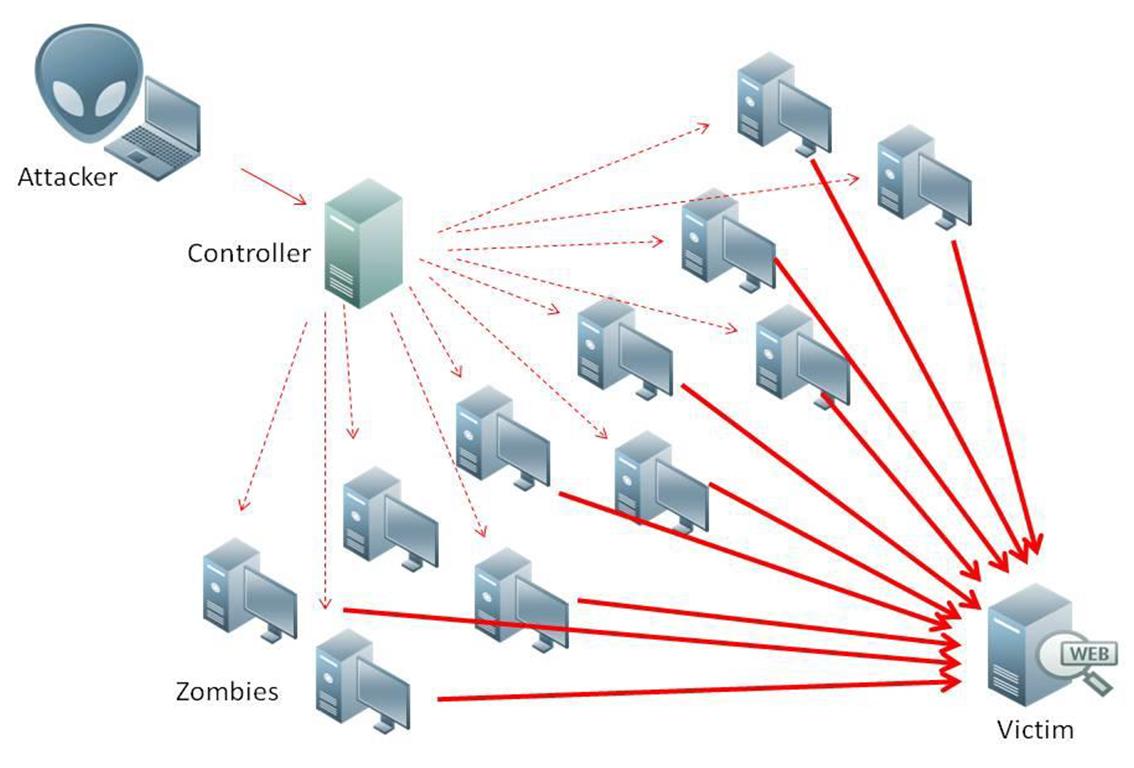
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
A DDoS attack at its core is the denial of access to a server or resource by means of causing a tidal wave of activity. The end result of an attack is to disrupt and to deny the resource to others. Most attacks are measured in the amount of activity generated.
The goal of a DDoS is to inflict financial damage upon a company by either exacting a ransom, inflicting loss of income and/or inflating operating costs. You can even watch this happen live via DigitalAttackMap.com. There are a few services available that can mitigate DDoS attacks via blocking illegitimate traffic, but this is one of the few attacks that you are rather powerless against.
Phishing/Spear-Phishing
Phishing is the act of sending out an email or other communication impersonating some other person or entity; it is usually done en-mass and does not target a specific person or organization as a victim. The goal is to cast a net as wide as possible and see how many people fall for the trap.
Spear-Phishing is the opposite. Spear-phishing involves targeting someone or a group of specific people in an attempt to exact information from them. This could include passwords, client information, or personal information. These often occur by email as someone posing as a supervisor or co-worker asking you to forward them some information.
The way to defeat this is to be vigilant with your email and communication policies and to have strong passwords for email accounts to prevent others from gaining access.
Spear-Phishing is the opposite. Spear-phishing involves targeting someone or a group of specific people in an attempt to exact information from them. This could include passwords, client information, or personal information. These often occur by email as someone posing as a supervisor or co-worker asking you to forward them some information. The way to defeat this is to be vigilant with your email and communication policies and to have strong passwords for email accounts to prevent others from gaining access.
Backdoors
A backdoor is a code-exploit where a person uploads and executes a piece of code to a server that allows them to gain access to that server. Backdoors are problematic as the person who installs this backdoor can use this as a foothold to execute other malicious code which escalates their powers on the server until they can essentially operate the server as if it was their own.
You will see this happens from time to time with popular CMS sites such as Joomla and WordPress, as these platforms are very popular and are actively researched for weak points. These types of cyberattacks are the worst-case scenario as there is no recovery from this attack. The only option that is feasible is to reformat the disk and start all over again, as nothing can be trusted.
You will typically see backdoors used in conjunction with a DDoS attack, as the backdoor allows the server to act like a zombie in a botnet, causing it to be a participant in an attack against someone else. Backdoors are somewhat preventable but it requires diligence in maintaining a secure environment where only permitted users are able to upload files.
Ransomware
Ransomware is software that is installed on your computer and causes your files or your computer to be taken over unless you pay some organization a “fee” or ransom to get back your PC and/or your files.
This type of attack is the evolution of the old malware issue that many of us faced back in the early 2000s with pop-up ads. Ransomware is typically a result of carelessness with downloading files from websites or as a result of a Phishing attack.
You’ll commonly see ads for software scanners promising to find out some malady to your system, but, in reality, they end up delivering all your files and private information to some overseas entity. Fighting ransomware is easy: don’t download anything that isn’t from a trusted source. For example, you may come across some page telling you that your version of flash is out-of-date and asks you to download the newest version.
The ONLY place you should trust is any link from adobe.com, the creators of Flash. Any other link or domain is probably a fake and installing it would be a coup de grace upon your computer. Fighting ransomware is easy: don’t download anything that isn’t from a trusted source. For example, you may come across some page telling you that your version of Flash is out-of-date and asking you to download the newest version. In this case, the ONLY download you should trust is a link from adobe.com, the creators of Flash.
Any other link or domain is probably a fake and installing it would be a coup de grace upon your computer.
Brute Force Logins/Password Attacks
A brute force password attack is where a bot tries a variety of common usernames and passwords against a system in an attempt to find a match. This is why you don’t set the passcode for your luggage as “12345.”
These attacks are commonly used against administrator accounts hoping to find the foolish person who set their account password to be “password” or “admin.” Simply using strong passwords and rotating passwords periodically will eliminate this type of threat. However, there’s also a caveat with a password attack: password re-use.
Back in September 2016, Yahoo had probably one of the worst leaks in history as information for over half a BILLION accounts was stolen from its server. In 2012, LinkedIn was the next victim to have their data leaked.
The goal of these attacks was, basically, to have a database of usernames, emails, and passwords, as well as other information that can be sold-off. If you use a common email/username and password for your Amazon,
Facebook and Netflix accounts, someone who finds out the password for one of them now can try that combination to gain access to all of your accounts. This is why you should have a separate and unique password for each service you use. If you find it hard to remember so many logins, then I suggest you use a tool like KeePass or 1Password.
So What Have We Learned?
The currency of the internet is information. Despite the dangers, most of these risks can be mitigated through proper security protocols.
By utilizing strong passwords and being vigilant of your internet activity, you can drastically reduce the opportunities that will make you vulnerable to these common types of cyberattacks.

