What Is BIMI? (Brand Indicators for Message Identification)
- Branding
- Email Marketing & Automation
- Hosting & Maintenance
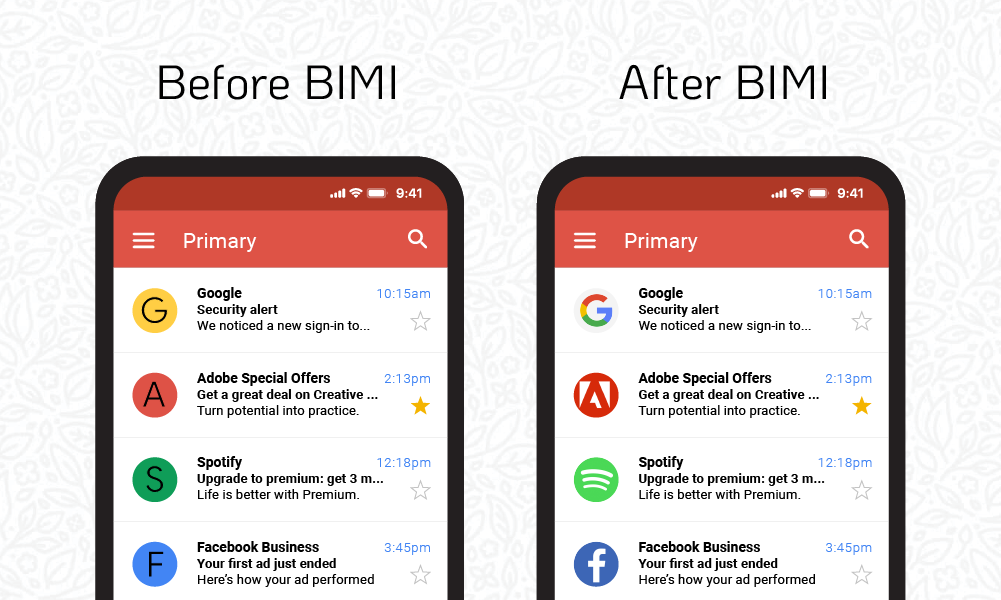
If you’re familiar with the world of email marketing, you’ve probably heard about the Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI) specification and are excited to try it out for yourself. Having your company’s logo on display next to each email you send? Pretty sweet!
As you begin to research how to set up BIMI email authentication, however, you may find yourself overwhelmed by the technical requirements. Most documentation around email security is written for web developers already familiar with the subject, not your typical marketing professional or business owner.
Yes, you will probably still need help from an IT Specialist to implement SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and BIMI, but you don’t need one to understand what those terms are and why they’re important. This blog will explain all the basics of authenticated email, so you can be one step closer to setting up your own BIMI email marketing.
What is Email Authentication?
Email authentication is the process and practice of confirming an email actually came from the person or business it alleges to be from. Setting up email authentication is important for keeping your sender rating and deliverability rates high .
It’s the responsibility of the brand’s domain to make sure they aren’t being impersonated by malicious actors. How do you accomplish this? By putting in place a series of rules and parameters that must be met for an email that claims to be sent on the domain’s behalf to actually be delivered to the recipient’s inbox.
Specifically, you will need to add TXT records to your DNS server(s) and SMTP server(s) to set up your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC specifications. (We’ll break all that jargon down for you next.)
What Is a TXT Record?
TXT records (short for text records) are strings of characters (letters, numbers, and symbols) meant for human-readable purposes. They are also used now by applications to read data (for example, domain ownership verification checks).
What Is a DNS Server?
A Domain Name System server tells your browser and others servers where resources (such as a website) are located. Typically, you can access your DNS configuration by logging in as an administrator on GoDaddy, Bluehost, or wherever you purchased your domain. Or, you may have an external vendor manage your DNS such as AWS or CloudFlare. You (or a trusted developer) can add TXT records here.
What Is a SMTP Server?
A Simple Mail Transfer Protocol server is used to distribute outgoing and incoming email (you can think of them like a mailman). In most cases, this server will belong to a 3rd-party email service provider you’ve set up an account with, like MailChimp, ConstantContact, or ActiveCampaign.
What is SPF?
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is an email authentication open standard based on a list of allowed IP addresses or hostnames your emails can be sent from. You can think of SPF like a bouncer outside of an exclusive club; if the sender’s IP address isn’t on the list, the email won’t pass the authentication check.
For example, here is the SPF TXT record for towermarketing.net:
"v=spf1 include:relay.mailchannels.net include:_spf.google.com ip4:192.241.241.153 ip4:192.241.244.84 ip4:198.199.78.17"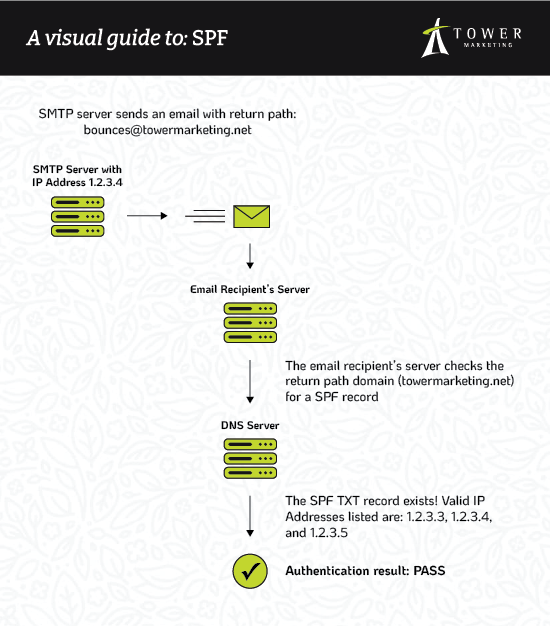
What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an authentication method that uses encryption to ensure your message content hasn’t been tampered with.
To set up DKIM, you must first create a pair of keys: one public and one private. There are several third-party tools you can use to generate these keys, or you may be able to create them through your email service provider.
The public key is added as a TXT record to your DNS server. Here is an example of a public key:
v=DKIM1;t=s;p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA7PMp1AWOJW5PnLA7Z5iW55kDbGImt3R7iZ4mykO4dhxLgm7ePK7vBurVCyY1thnAH3ZuBRgwRNjq/2awWHDGkQqvmrKoHWl8PE72aayHh0QorOZJEWG3b9rRruglIVKKKQ7y59Q0fEbFKIjSUFJFOr/tmEjWN5aMsQkULbazzJDRhGdatymabJGfBUX9nI4PDVoIwEkqt/7iDsLaSyur769RxFeHW/39tDSmt6Mpg20m3VmKWjVXdXyLQKn+vEtZYT2zlgfpkV8NIQJGBrzo6FPk14e7xbG5E5RbblLo7fPwOvzJSht90UJV0vrAoDPdwekj2OMuQfSbZIZDfzkY2wIDAQABThe private key, stored on your SMTP server or with your email service provider, is used to generate a signature before the email is sent. This signature is comprised of several parts, but the header and body content are converted into unique strings of letters and numbers called “hashes .” These hashes are then used in the encryption, decryption, and validation processes to prove the content is legitimate and has not been modified by someone else before it arrives in your inbox.

What is DMARC?
Your DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) policy is a TXT record added to your DNS server. It is used by a sender to indicate their messages adheres to SPF and DKIM, and provides instruction to the recipient with what to do with an email that isn’t authenticated by SPF and DKIM. It can be set to one of the following:
- None: Do nothing and allow the email into the inbox even though it failed authentication. For obvious reasons, this is not a recommended approach.
- Quarantine: Send the email to the spam folder.
- Reject: Do not deliver the message at all.
In addition to checking the pass or fail results of SPF and DKIM, DMARC adds an extra layer of security by ensuring that the email’s sender domain (in our case, towermarketing.net) is the same as the email address listed in the DMARC record.
Here is an example of a DMARC record:
"v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:leads@towermarketing.net"If you’re like me, it helps to have a visual aid when trying to understand a complex topic like authentication. Learndmarc.com provides step-by-step explanations and examples of SPF, DKIM and DMARC in action.

What is BIMI?
Brand Indicators for Message Identification (pronounced bih-mee) is an industry specification for message identification that builds on your DMARC policy. If your email passes SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication, you can then set up BIMI to display your pre-approved logo in inboxes that support this functionality.
BIMI is the brainchild of The AuthIndicators Working Group, a collection of companies including Fastmail, Google, Mailchimp, Proofpoint, Twilio SendGrid, Validity, Valimail, and Verizon Media (the owners of Yahoo). Their joint goal is to improve inbox security and reduce fraudulent messaging by making authentic emails instantly recognizable.
BIMI is a way of rewarding people for putting in the hard work of securing their emails by allowing them to put their brand’s logo on display. This also builds brand recognition and trust with your email recipients.
In part two of this blog, I’ll explain all the specifics of setting up BIMI for yourself.
Before you jump into the world of SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and BIMI, it’s important to understand the basics of email marketing. Creating a strategic plan, a healthy customer list, and relevant messaging are all keys to success–and if you need some help, Tower has you covered.
 By Danae
By Danae  Kelly H
Kelly H